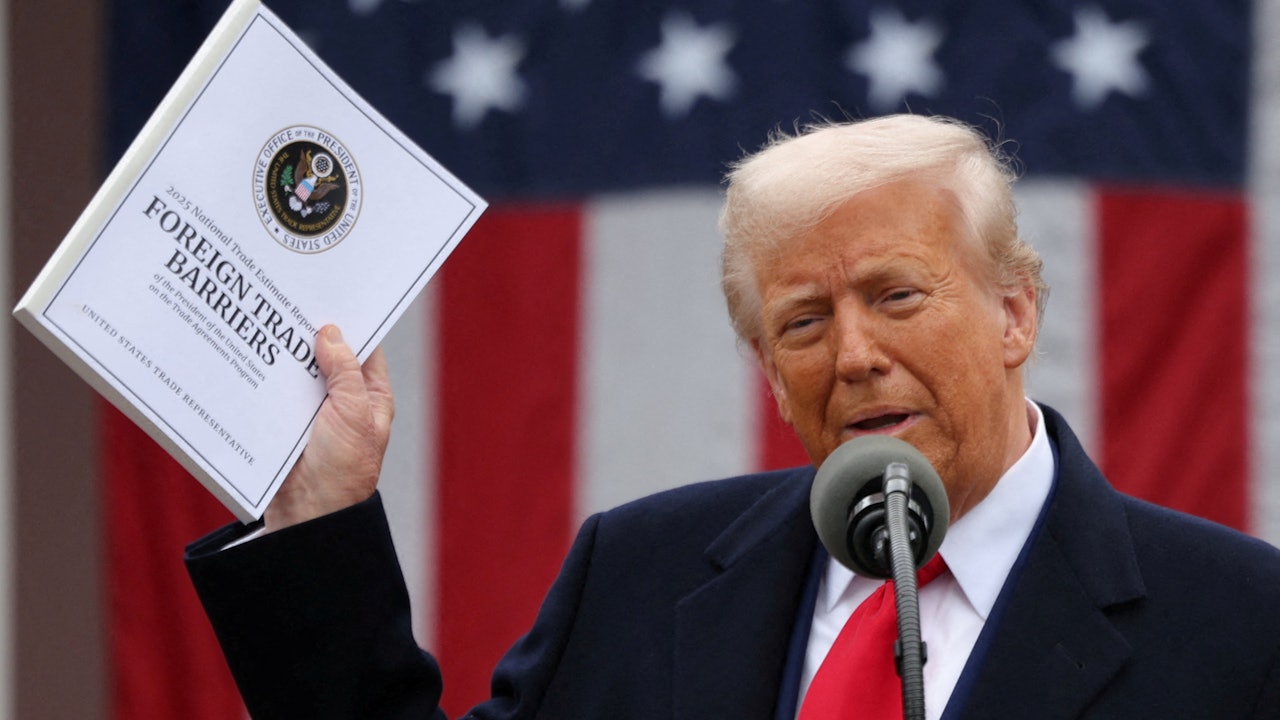
美國總統特朗普 recently announced plans to impose tariffs on imported chips and pharmaceuticals, sparking widespread discussions in the global trade community. The U.S. Department of Commerce has initiated investigations into the impact of importing semiconductors, semiconductor manufacturing equipment, and pharmaceuticals on national security. This move reflects the Trump administration’s continued emphasis on reshoring critical industries to enhance domestic production capabilities. The investigations, conducted under Section 232 of the Trade Expansion Act, are expected to influence U.S. trade policies and potentially lead to new tariffs on these products.
The decision to investigate the importation of semiconductors and pharmaceuticals is rooted in concerns over U.S. reliance on foreign suppliers. Semiconductors, often referred to as the “brains” of modern electronics, are crucial for a wide range of industries, including defense, telecommunications, and automotive manufacturing. The U.S. has long been a leader in semiconductor technology, but in recent years, countries like China and South Korea have significantly increased their production capacities. The administration fears that over-reliance on foreign semiconductors could jeopardize national security in the event of a supply chain disruption or geopolitical conflict.
Similarly, the pharmaceutical industry is a critical area of concern. The U.S. imports a substantial portion of its active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and finished drug products, with many of these imports coming from countries like India and China. The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the vulnerabilities in global supply chains, including those for medical supplies and pharmaceuticals. By investigating the importation of pharmaceuticals, the U.S. aims to assess whether its reliance on foreign manufacturers could threaten public health and national security.
The investigations also signal a broader shift in U.S. trade policy under the Trump administration. The administration has consistently prioritized protecting domestic industries and reducing trade deficits. Previous tariffs on Chinese goods, imposed under similar national security concerns, have led to significant changes in global trade dynamics and prompted retaliatory measures from trading partners. The new investigations into semiconductors and pharmaceuticals are likely to further strain international trade relations, particularly with major exporters like China and India.
In addition to national security concerns, the investigations may also have economic implications. Imposing tariffs on imported semiconductors and pharmaceuticals could lead to increased costs for U.S. manufacturers and consumers. However, the administration argues that these measures are necessary to ensure long-term economic and national security. The investigations could also incentivize domestic production by making imported goods more expensive, potentially creating jobs in the U.S. semiconductor and pharmaceutical industries.
The U.S. Department of Commerce has emphasized that the investigations are in line with the administration’s commitment to fair and reciprocal trade practices. The findings of the investigations will likely influence future trade policies and may result in new tariffs or other trade restrictions. The outcome of these investigations will be closely watched by global markets, as they could significantly impact supply chains and trade relations.
In conclusion, the U.S. Department of Commerce’s decision to investigate the importation of semiconductors and pharmaceuticals under Section 232 of the Trade Expansion Act reflects the administration’s ongoing efforts to address national security concerns and reshape global trade dynamics. While the investigations aim to enhance U.S. self-sufficiency in critical industries, they also carry potential economic and geopolitical consequences. The results of these investigations will undoubtedly play a key role in shaping U.S. trade policy in the coming years.
美商務部以國家安全為由,啟動對藥品和半導體進口調查